|
Test/Observation |
Specifications |
Result |
|
Assay (C10H16N2O3S) |
98% |
99.62 % |
|
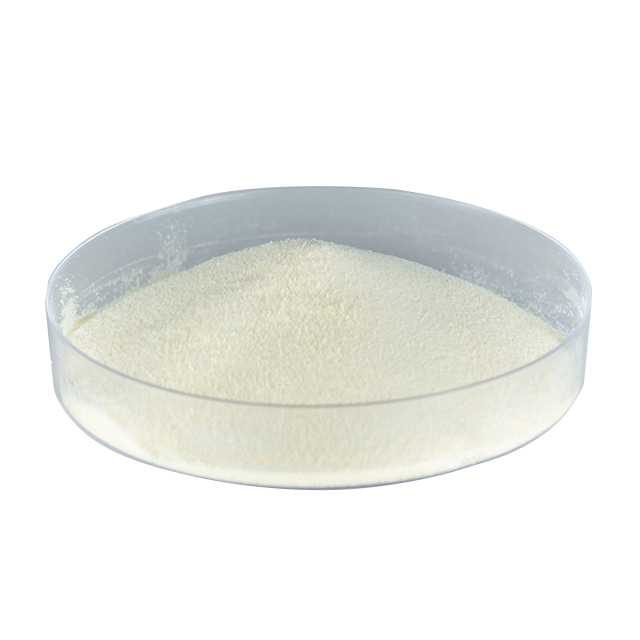
Appearance |
White Crystalline Powder |
Complies |
|
Odor & taste |
Characteristic |
Complies |
|
Specific Rotation |
89o_ 93o |
91.7o |
|
Organic Volatile Impurities |
Meets the requirements of USP 30 |
Complies |
|
Sulphate Ash |
0.1% |
0.08% |
|
Loss on drying |
MAX. 1% |
0.32% |
|
Restdue on ignition |
MAX. 0.1% |
0.33% |
|
Heavy metals (PPM) |
MAX.20% |
Complies |
MicrobiologyTotal Plate Count Yeast & Mold E.Coli S. Aureus Salmonella |
<1000cfu/g <100cfu/g Negative Negative Negative |
42 cfu/g 6 cfu/g Complies Complies Complies |
|
Conclusion |
|
|
|
Conform with specifications of USP 35 |
|
|
Biotin is necessary for cell growth, the production of fatty acids, and the metabolism of fats and amino acids. It plays a role in the citric acid cycle, which is the process by which biochemical energy is generated during aerobic respiration. Biotin not only assists in various metabolic reactions but also helps to transfer carbon dioxide. Biotin may also be helpful in maintaining a steady blood sugar level. Biotin is often recommended for strengthening hair and nails. As a consequence, it is found in many cosmetics and health products for the hair and skin, though it cannot be absorbed through the hair or skin itself.
How does it work?
Biotin is an important component of enzymes in the body that break down certain substances like fats, carbohydrates, and others.
There isn’t a good laboratory test for detecting biotin deficiency, so this condition is usually identified by its symptoms, which include thinning of the hair (frequently with loss of hair color) and red scaly rash around the eyes, nose, and mouth. Nervous system symptoms include depression, exhaustion, hallucinations, and tingling of the arms and legs. There is some evidence that diabetes could result in biotin deficiency.
Application:
- Treating and preventing biotin deficiency. Symptoms of deficiency include thinning of the hair (often with loss of hair color), and red scaly rash around theeyes, nose, and mouth. Other symptoms include depression, listlessness, hallucinations, and tingling in the arms and legs. There is some evidence that cigarette smoking may cause mild biotin deficiency.
- Skin rash in infants (seborrheic dermatitis).
- Hair loss. There is some preliminary evidence that hair loss can be reduced when biotin is taken by mouth in combination with zinc while a cream containing the chemical compound clobetasol propionate (Olux, Temovate) is applied to the skin.
- Diabetes. Biotin alone doesn’t seem to affect blood sugar levels in people withtype 2 diabetes. However, there is some evidence that a combination of biotin and chromium (Diachrome, Nutrition 21) might lower blood sugar in people with diabetes, whose diabetes is poorly controlled by prescription medicines. Other early evidence shows that the same combination reduces ratios of total cholesterol levels to “good” high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, “bad” low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol to HDL cholesterol, and non-HDL to HDL cholesterol in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Diabetic nerve pain. There is some evidence that biotin can reduce nerve pain in people with diabetes.
- Brittle fingernails and toenails. Biotin might increase the thickness of fingernails and toenails in people with brittle nails.